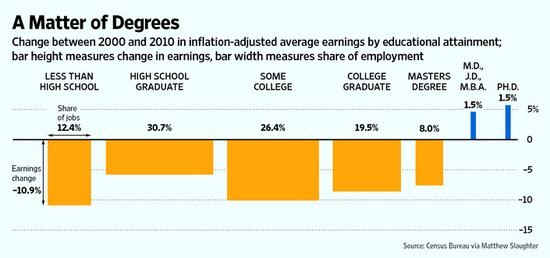
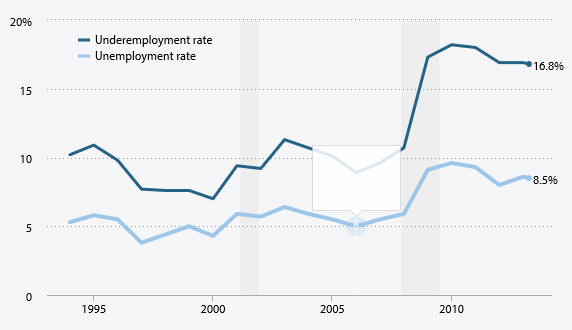
VII.
Income elasticity
is the % change in quantity demanded divided by the % change in income.
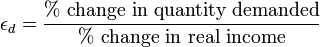
A. Income elasticity is positive for normal (superior)
goods such as steak
and vacations - more is purchased as income
increases.
B. Income elasticity is negative for
inferior goods such as bread and
hamburger-less is purchased
as income increases.
C. In times of recession, income
elasticity determines
loss in
revenue by
producing
firms.
D.
Selected
income elasticity's Wiki
E. Income Elasticity of Demand
F. Visit
Income
Elasticity of Demand from tutor2u for
more information.
VIII. Cross elasticity
of demand
is the % change in quantity demanded
divided by the % change in the price of a substitute or complement.
A. Cross elasticity is positive
for goods that are substitutes (price of hot dogs up,
quantity of hamburger sold up).
B. It is negative for goods
that are complements (price of hot dogs up, quantity of hot
dog rolls sold down).
C Near zero for independent
goods (peanuts and grapefruit)
C. Cross
Price Elasticity of Demand from tutor2u
D.
Income
and Cross Elasticity Video from ACDC Econ
E. Virtual
Economy from Buz\ed
has an elasticity calculator. Please
IX. Price elasticity of supply is the % change in quantity supplied divided by the %
change in price.
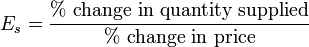
A. It is a function of how factor costs
change as more is produced and the passage of time.
B. If costs (factor prices such as wages
and rent) change little as more is offered for sale at higher selling prices
then profit potential is high and supply will be
elastic.
C. Supply elasticity also increases with
time as companies have more time to adjust to higher costs.
1. Unusually high
demand for tomato's or the Chrysler PT Cruiser take time to produce and supply is
inelastic.
2. Gateway may be
able to increase the number of a new popular
model computer quickly and supply
is more elastic.
D. Gold production is costly and takes time so
price is volatile because of frequent demand changes.
E.
Selected
supply elasticity's
F. Visit
Price elasticity of supply
from tutor2u for more information
A. Effect on tax incidence
B. History of Price Elasticity- Wiki
C. Why Current Methods to Combat Climate Change Don’t Work
D. Economic Surplus of consumers and producers is explored in the next chapter.

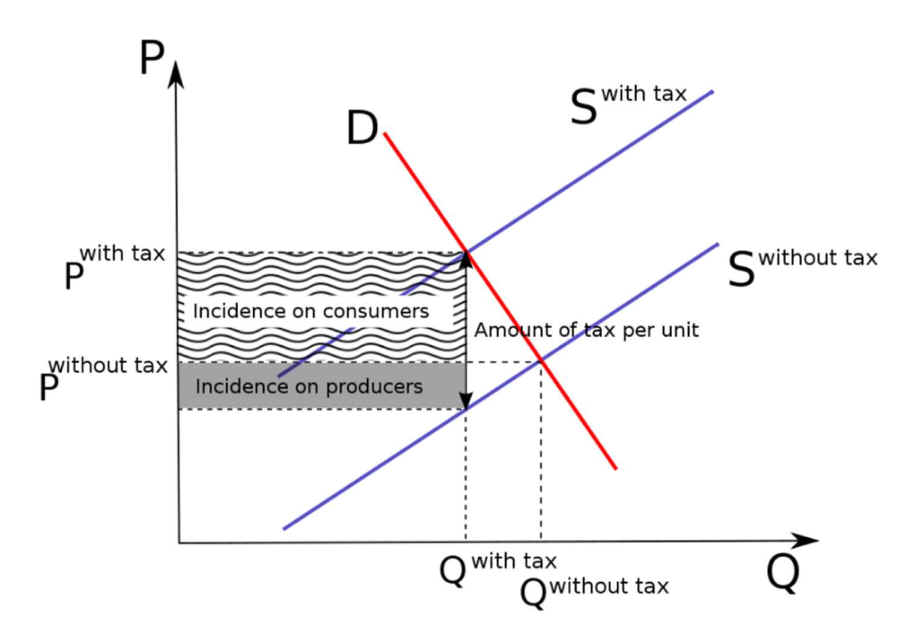
 B. Price is up much more than
B. Price is up much more than