|
IV.
Law of Increasing Opportunity Costs
1. Opportunity costs usually increase.
a. To have one unit of A you must give up amount
x of B.
To have a
second unit of Item A you must give up more
than amount X
of B.
b. Examples
1)
Training more people in math and science would increase
productivity
for a while but eventually people would be
trained
to be
engineers who would be more productive
as
managers, teachers, or
entertainers etc.
2) The gain from replacing people with machines may be
large
in the beginning but
eventually machines would
be used to
do
what people can do
more efficiently.
a. When
opportunity costs are not increasing, the
production possibility
curve is a straight line. High tech
investment may even bend the
curve the other way
and have decreasing cost, but not forever.
b. Below
is an example of the trade-off
between investing
people in high tech industries versus entertainment
industries. Suppose you have 10 entertainers and no
technicians.

d. Law
of Increasing Opportunity Cost video
2min
2.
Quiz
with answers and
What are the opportunity costs of the
Trans-Pacific Partnership?
Unit IV.
Review Having additional units of A
requires giving up more and more of B.
|

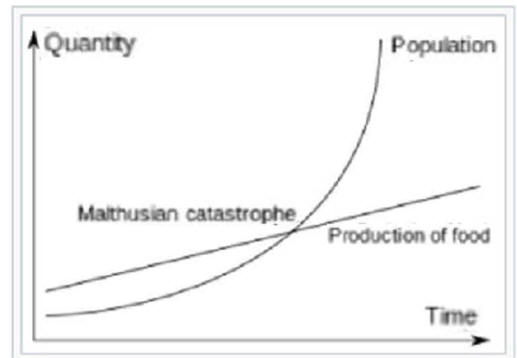
Eventually Increasing
Opportunity Cost
Can Be Painful,
but Some Have an Excuse!

3. Readings and Videos
a.
Production Possibilities Curve
Constant and Increasing Opportunity Cost
b.
Amos WEB has more.
c.
Factors of Production
d.
Economics of the Trans-Pacific Partnership
e.
Opportunity Costs, - the parable of the broken window
|