I. Introduction
A.
Part II Product and Factor Markets
gives an overview of micro Markets
B. A monopoly exists when one
firm has continued control over a unique market.
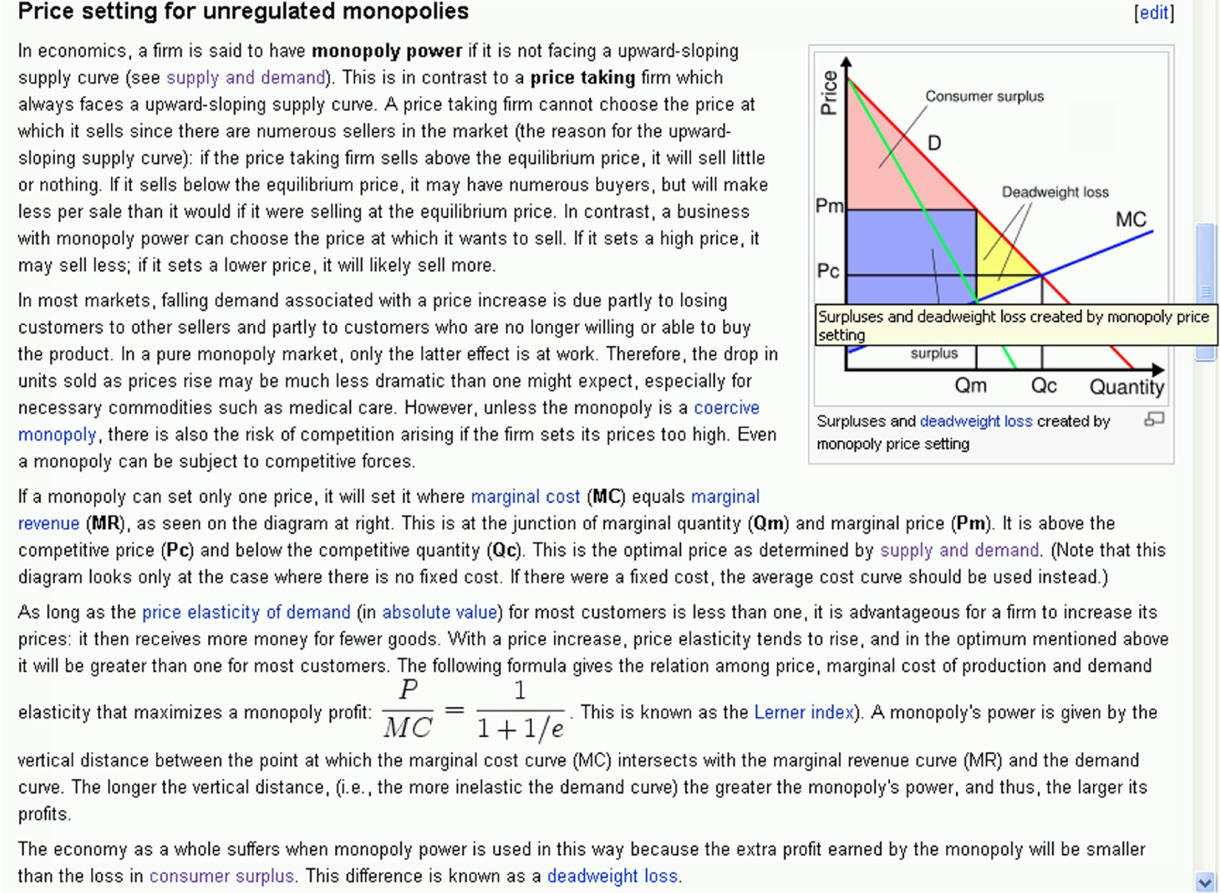
1. By controlling supply
and therefore price, a monopoly may earn high
economic profit.
2. Continued existence presupposes
barriers which restrict market entry and
the
resulting competition.
D. Barriers to entry
1.
Economies of scale require
a.
Large initial capital investment
b.
Large R & D expenditures
2. Ownership of
raw material, strategically located land, etc.
3. Patents and
copyrights
4. Unfair
competition
5. Natural
barriers to entry lead to natural monopolies.
a.
Economies of scale can be so large that more than one
producer is illogical.
b.
Natural monopolies reduce duplication, waste, and confusion.
c.
Natural monopolies are often privately owned and publicly regulated.
d.
Example: public utilities
e. 1980's,1990's
deregulation lowered the importance of natural
monopolies.
6.
Inside Big Tech's DC Washington Survival Strategies
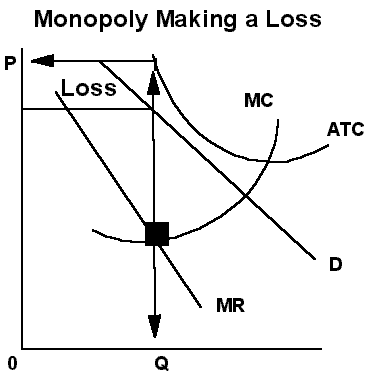
III. Some Monopolies Make No Profit.
A. Rising costs and shrinking demand may result
in
a monopoly not making a profit.
B. When this happens, demand (average revenue)
is always below the ATC and a loss results.
IV. Some Monopolies are Regulated.
A. If demand is inelastic, profit may be excessive.
B.
Price Discriminating Monopoly Micro in 60 seconds
C. Government regulates with antitrust laws, government
ownership, and
limiting profit by restricting price to ATC.
D. M is the where monopoly maximizes
profits.
E. Regulated price R yields a normal
return.
F. E is the economically optimum price.
G.
Econ in 60 Seconds Video: Regulating a Monopoly

|
II.
Most Monopolies Make a Profit.
A. ATC includes normal return on investment.
B. MC cuts ATC at lowest point.
C. Profit is maximized by producing a quantity and charging a price
indicated by the intersection of MC and MR.
D. The resulting profit is not a payment for enterprise, it is economic
rent which should not
exist in pure capitalism.

1. Economic
Rent
2. Rent
Seeking
3. Economic
Rent Video 7:47
E. High inelastic demand will result in a higher price, greater profit,
and more restricted (smaller) quantity.
F.
Econ in 60 Seconds Video on Mmonopoly
Graph Review
V. Economic
Analysis of Monopoly
A. With pure competition
1. P = MR = MC
2. Production is at
the lowest point on ATC curve.
B. With Monopoly
1. P > MR = MC
2. Production is not at the
lowest point indicated
by the ATC curve
3. Quantity produced is restricted.
C. A monopoly is a price maker.
D. Are monopolies inefficient
1. There are many
inefficiencies.
a. Lack of competition makes monopolies
wasteful as nothing forces efficiency.
b.
Advertising just to enhance barriers to entry.
c.
Litigate to protect monopoly power
d.
Active politically to protect monopoly power
2. Large scale efficiencies
a.
Bigness creates efficiencies (economies of
scale)
causing the ATC curve to be below
that of pure
competition.
b.
Creates the necessary profit and profit potential
required for investors to assume the risk associated
with large capital investment requirements including
ever-increasing R & D expenditures.
E. Additional Materials
1.
When Monopoly Wasn't A Game.
2.
2012
AP Econ Video-We're a Monopoly, Arab Money
3.Big 2002 recording stars exhibit monopoly power
Source
The Big Picture
Paul McCartney, $103.3 million
The Rolling Stones, $87.9 million
Cher, $73.6 million
Billy Joel/Elton John, $65.5 million
Dave Matthews Band, $60.1 million
Bruce Springsteen & the E Street Band, $42.6 million
Aerosmith, $41.4 million
Creed, $39.2 million
Neil Diamond, $36.5 million
The Eagles, $35.4 million |